Image source: researchgate.net
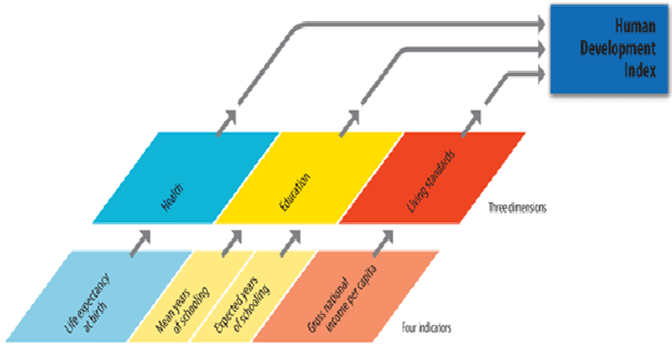
The human development index is a measure of the country’s economic development and its economic welfare. It examines the life expectancy at birth, education, and income levels of people measured by the GDP per capita and adjusted according to the purchasing power parity (PPP).
The economic growth of the country may not be sustainable if it leads to inequalities and negative impacts on society. Let’s look at the pros and cons of the Human Development Index to help you understand more about wealth and economic development.
Pros:
1. Wide use: HDI indicators are used worldwide. Countries use HDI to compare their level of economic development and global economic patterns.
2. Increased infrastructure: Increase in the education level and health of individuals leads to an improvement in the country’s infrastructure.
3. Balance in human development: HDI not only concentrates on economic development but also looks at other areas to measure human development like social measures and individuals’ health.
4. Question national policies: HDI can enable policymakers in the country to easily adjust and implement economic policies. It also helps question how countries with the same GNI per capita have different HDI.
5. Accuracy: It takes measurement in three areas; health, education, and income level making it more accurate.
6. Reliable: HDI is more reliable since it involves more than economic development but also looks at the standards of living and level of literacy in measuring the country’s development making it more reliable.
7. Measures per person contribution: HDI uses GDP per capita measures to determine the average contribution or gain of each individual in economic welfare and development instead of using GDP.
8. Determines areas that need urgent attention: HDI data enable the government to know areas that need immediate attention and also to come up with appropriate measures for development.
9. Allocation of funds: Government can use HDI data to allocate funds in development projects or seek financial aid from the international market to develop underdeveloped areas.
10. Measure the country’s status: HDI measures the social-economic development of the country in various aspects.
Cons:
1. Wide divergence among countries: Different countries have different HDI scores and access different groups differently resulting in wide divergence within the countries.
2. Reflect on long-term changes: HDI focuses mostly on the long-term changes in the country like the life expectancy of people and has less response to short-term changes.
3. No clear indication of the country’s welfare: There is no correlation between having a higher national wealth and the welfare of the country. GNI is directly proportioned to how it is spent and may not increase economic welfare.
4. Measure data on a few areas: HDI doesn’t put other factors like gender equality, death rate, poverty, and wealth distribution into consideration when measuring economic welfare and development.
5. No standard education index in society: There is no clear indication of the level of education on all the groups of people in the society. It is difficult to measure whether poor families can access primary, secondary, tertiary, and high education in society.
6. Increases inequality: Sometimes spending more on gross national investments (GNI) per capita can hide the widespread inequality within the country. Higher GNI results in high levels of inequality.
7. Depends on some factors: Economic welfare depends on access to clean water, the threat of war, levels of population among others.
8. Unequal distribution: There is a lot of criticism that the GDP doesn’t measure unequal distribution within the country thus giving an inaccurate level of economic development.
9. Arbitrary measures: There are various ways of measuring the health or life expectancy and education levels thus, making some of the chosen measures to be arbitrary.
10. Lack of consistent: Most countries do not release data required to calculate the HDI on yearly basis thus lacking year-to-year consistency.